drop arm test for shoulder|drop arm test interpretation : bulk passively elevate arm in scapular plan to 90°. Then ask the patient to slowly lower the arm. The test is positive when weakness or pain causes them to drop the arm to their side. Resultado da 10 de nov. de 2022 · Himawari and Hinata 1 (Pixiv Fanbox) Himawari and Hinata 1. (Pixiv Fanbox) Published: 2022-11-10 13:00:00. Imported:
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBZoey descobre um aplicativo mágico que pode controlar os meninos em sua vida.
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.
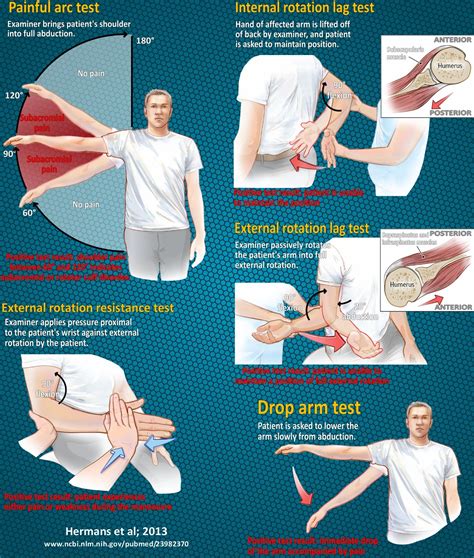
The Drop Arm Sign or Drop Arm Test is a common orthopedic test to assess for full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus. The drop arm test is a commonly used diagnostic tool to assess shoulder instability. It involves a combination of the patient's arm being abducted and then slowly . passively elevate arm in scapular plan to 90°. Then ask the patient to slowly lower the arm. The test is positive when weakness or pain causes them to drop the arm to their side.Codman's test is typically used in the assessment of a suspected rotator cuff tear. This test is also commonly referred to as the drop-arm test or sign.
The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tears. To perform the Drop Arm test, position the patient in sitting or standing with the arm relaxed at their side. Codman's Test, also known as the Drop Arm Test, is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess for rotator cuff pathology. Evaluate the ability to maintain shoulder abduction, indicating possible rotator cuff tear or dysfunction.
This is a really great test for you to use with your patients who you suspect may have injured their Rotator Cuff, and in particular, may have suffered a Rot.Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. Test Position: Sitting or standing Performing the Test: The patient is told to actively elevate the arm in the scapular plane, followed by slowly reversing the .
The drop arm test is designed to determine a patient's ability to sustain humeral joint motion through eccentric contraction as the arm is taken through the full motion of abduction to adduction. . Examiner will passively abduct the patient's shoulder (humerus) to 90 degrees. The patient is then asked to slowly lower or adduct the shoulder to .
Drop-arm test. How it’s performed: . How it’s performed: A doctor will stabilize your arm at the shoulder while gently pulling on your arm. What it tests for: Shoulder instability. Kathleen Carr, MD demonstrates the Drop Arm Test as part of a complete Shoulder ExamThe aim was to assess diagnostic accuracy of 15 shoulder special tests for rotator cuff tears. From 02/2011 to 12/2012, 208 participants with shoulder pain were recruited in a cohort study. Among tests for supraspinatus tears, Jobe’s test had a .
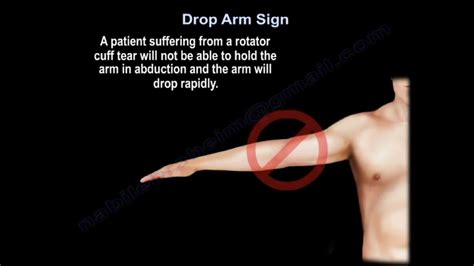
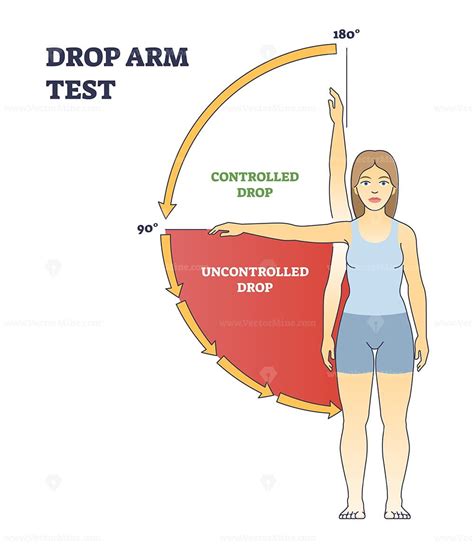
As Prices Drop, Point-of-Care Ultrasound May Spark Evolution of Physical Exam . ask the patient to flex the arm at the shoulder by moving the upper extremity anteriorly and then superiorly, until it is above the head. . To perform this test both the elbow and the shoulder should be flexed at 90°. The examiner must support the arm of the . 2. Drop Arm Test. A rotator cuff tear will make it difficult for you to control your arm as it lowers, especially if any one of the 4 stabilizers of the rotator cuff are compromised. To perform the drop arm test, simply raise your arm overhead in an arc, with as much range as possible. Now reverse the arc and lower your arm slowly, without . In summary, the indications for performing a drop arm test include shoulder pain, limited range of motion, and weakness. It is a valuable diagnostic tool that can help identify a rotator cuff tear or weakness in the shoulder. However, it is important to interpret the results of the test in conjunction with other clinical findings and imaging . - Push off demonstrating winging of scapula - Apley scratch tests for shoulder motion - Drop arm test - External rotation testing of shoulder - Passive Painful Arc Neer Test - Scapular assistance maneuver - Sulcus sign for glenohumeral instability examination - Apprehension relocation release tests for shoulder
This Technique Peek video features Frank Hoeffner, DPT, OCS demonstrating how to perform drop arm test for the shoulder. This test is performed by passively .The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tears. How to Perform Drop Arm Test. Position of Patient: Patient is sitting or standing with arm relaxed at side. Performance: The examiner passively places the patient’s arm into abduction of 90 degrees. The patient is instructed .Drop-arm test: Active shoulder abduction to 90°, then return . Positive: Dropping the arm down with pain indicates a positive test; Drop Arm Test video provided by Clinically Relevant. Jobe/supraspinatus/empty can test: Resist shoulder abduction and internal rotation. Drop Arm Test . Your healthcare provider may perform the drop arm test if they think you may have a rotator cuff tear in your shoulder. For this test, the provider will lift your arm out to the side of your body while keeping it straight. .
The drop arm sign is often used to diagnose a rotator cuff tear. The examiner brings the arm to 90 degrees of abduction and instructs the patient to maintai.Performing the Test: Have patient actively abduct the shoulder to 90 0. If the patient is not able to actively abduct the shoulder, then the examiner should passively abduct the shoulder to 90 0 and ask the patient to hold the arm in that position. Next have the patient slowly adduct or lower the arm towards the body.
The patient's arm is passively elevated to 90 degrees in the scapular plane, by the examiner; The examiner passively flexes the elbow to 90 degrees; The patient is asked to actively externally rotate the shoulder against the examiner's resistance; Another method for performing the test, introduced by McClusky, helps depict the Hornblower's sign:Orthopedic Exam / Special Tests for Physical Therapy: SHOULDER Drop Arm Test: Rotator Cuff: In anatomy, the rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the shoulder. The four muscles of the rotator cuff are the supraspinatus muscle, the infraspinatus muscle, teres minor muscle, and the subscapularis muscle.The .Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Empty Can Test, also known as the Jobe or Supraspinatus test, is used to assess for lesions of the rotator cuff, specifically the supraspinatus muscle and supraspinatus tendon.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patients arm is actively abducted to 90 o; The examiner applies downward resistance to the abducted arm; With the patient's hand in . Drop arm test is an evaluation done to assess rotator cuff injuries. Read the article below to know more. Medical articles . can help distinguish between rotator cuff and shoulder diseases as well as diagnose subacromial discomfort syndrome or shoulder impingement. When the drop arm test is used for a series of experiments like these, it .
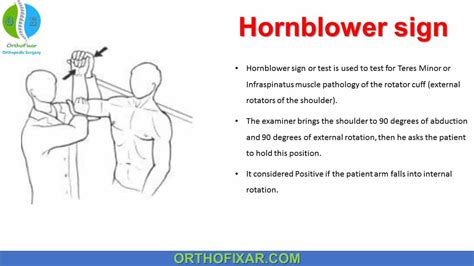
1. The patient is seated and the elbow is passively flexed to 90 degrees while the shoulder is held at 20 degrees elevation in the scapular plane in a position of near maximum external rotation (i.e., maximum external rotation minus five degrees to avoid an elastic recoil effect). If the patient is able to hold this position, this indicates a negative test.
positive rotator cuff tests
Codman's Test, also known as the Drop Arm Test, is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess for rotator cuff pathology. Evaluate the ability to maintain shoulder abduction, indicating possible rotator cuff tear or dysfunction.On the side to be tested, one of the examiner’s hands stabilizes shoulder girdle. The arm to be tested is moved into 90 degrees of forward flexion in the plane of the scapula . Drop Arm Test; Gerber’s Lift Off Test; Hawkins Test / Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Test; .
To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test. Evidence [ edit | edit source ] Based on the Park et al [1] study, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator .Drop Arm Test. The patient is either seated or standing. The examiner passively raises the arm to 90°. The patient slowly lowers the arm towards their side in the same plane with palm down. A positive test is pain, sudden drop of arm or inability to smoothly control the descent. The drop arm test, also known as Codman's sign, was performed with the patient standing . The patient was asked to abduct the arm fully and then to reverse the motion slowly, in the same arc. When the arm dropped suddenly, the test was considered positive. The drop arm test was developed specifically for the evaluation of the supraspinatus tendon.
In the drop arm test, the patient’s shoulder was abducted passively at 90°; the patient was then asked to slowly lower the arm in the same arc. The drop arm test was considered positive if the patient could not controllably lower the arm. We also performed other clinical tests related to the infraspinatus, subscapularis, and biceps muscles.
test for screen tearing
Resultado da Beatriz Rabuda. Trans. +5548998026530. 26 Anos. 172 CM. 85 KG. 18 CM. Nacionalidade Brasil. Cabelos Moreno. Corpo Fitness. Seios Grande. .
drop arm test for shoulder|drop arm test interpretation